Union Budget 2023
Introduction
The Union Minister of Finance and Corporate Affairs, Nirmala Sitharam, presented the Union Budget 2023-24 in Parliament on Wednesday. The Union budget was the 5th budget of Modi 2.0. Big boosters for taxpayers, railways, job creation and capex were announced. Nirmala Sitharaman also highlighted that the Indian economy is on the right path and headed towards a bright future.
Aim of Union budget 2023:
- Opportunities for citizens with a focus on youth.
- Growth and job creation.
- Strong and stable macroeconomic environment.
- Also enable women’s self-help groups to reach the next stage of economic empowerment.
- Similarly helping self-help groups with supplying raw materials, marketing products and branding.
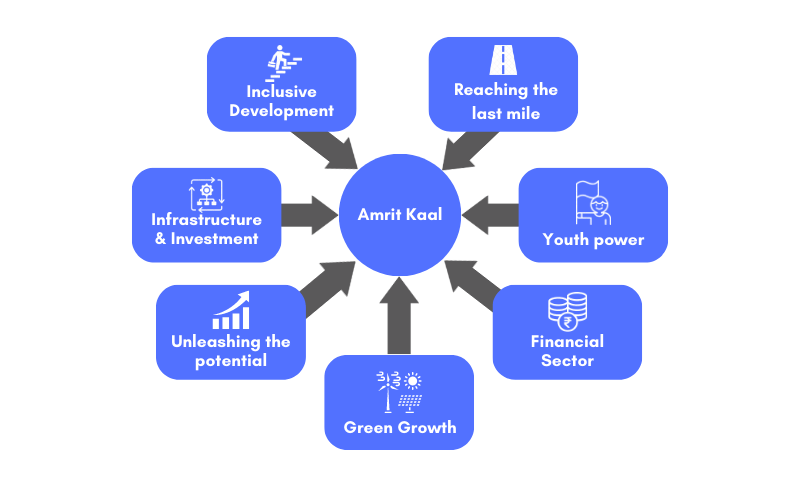
Seven priorities of Saptarishi
Major Highlights
- Per capita income has more than doubled to ₹1.97 lakh in 9 years.
- The Indian economy has jumped from the 10th to the 5th largest in the world in the past nine years.
- According to government estimates, the nominal GDP will grow by 10.5% in 2023-24.
- 7,400 crore digital payments of ₹126 lakh crore took place through UPI (Unified payments interface) in 2022.
- Around 220 crore Covid of 102 crore persons completed.
- EPFO (Employees provident fund organization) membership has more than doubled to 27 crores.
- 11.7 crore household toilets built under Swachh Bharat Mission.
- Similarly 47.8 crore PM Jan Dhan bank accounts.
- Insurance covers 44.6 crore people under PM Suraksha Bima and PM Jeevan Jyoti Yojana.
Main Tax proposal in the finance bill
- There have been changes to the income tax regime. There are now five tax slabs instead of six.
- A charitable trust must apply 85% of its income within a year to qualify for income tax exemption.
- Online game winnings will be subject to a 30% tax deductible at source.
- Capital gains from the sale of residential property can deduct to the extent of the purchase or construction of another residential property. The deduction will capped at Rs 10 crore.
- Income from investments in life insurance policies will be taxable if a premium of Rs 5 lakh is paid in any year.
- Moreover this extension allows startup companies to deduct up to 100% of their profits if they incorporate within this period and meet other conditions. Hence the end date of the deduction period extend from 31 March 2023 to 31 March 2024.
Direct Taxes
New Income tax slabs under new tax regimes:
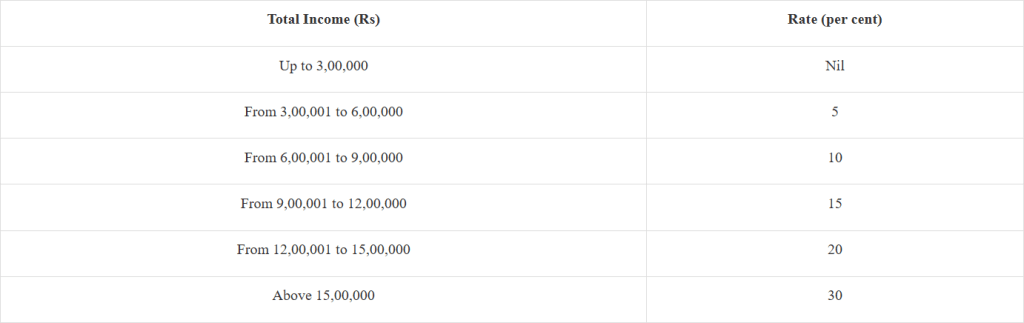
- An individual with an annual up to three lakhs will have tax exemption.
- Individuals with an annual income of 9 lakhs will pay 5% taxes.
- The annual income of 15 lacks will fetch Rs.1.5 lakh tax, i.e. 20%.
- Tax exemption removed in insurance policies with premiums more than Rs 5 lakh.
Indirect Taxes
- A total of Rs 15,29,200 crore is expect to collected in indirect tax in 2023-24. Thus the government estimates it will raise Rs 9,56,600 crore through GST.
- The number of basic customs duty rates on goods other than textiles and agriculture reduced to 13 from 21.
- Crude, glycerine basic custom duty reduced to 2.5%.
- Silver bars import duty hiked to align it with gold and platinum.
What gets cheaper

What gets costlier

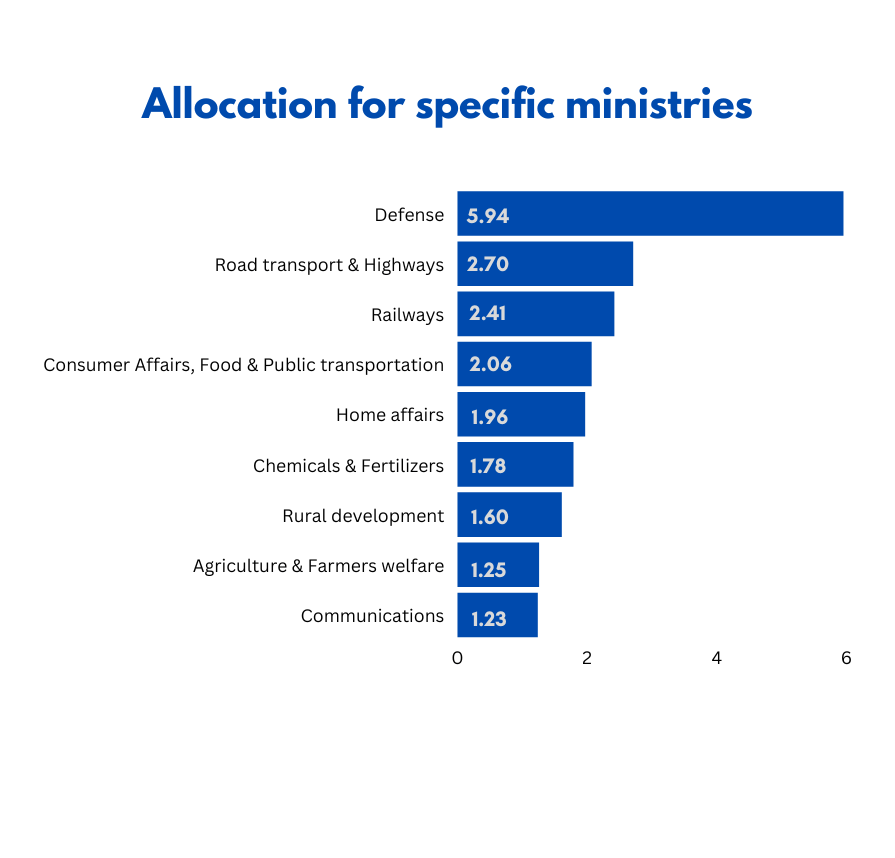
Allocation of specific ministries
Saving Schemes
- In the budget the maximum deposit limit for Senior Citizen Savings Scheme increase to Rs 30 lakh from Rs 15 lakh.
- Similarly the Monthly Income Scheme limit double to Rs 9 lakh and Rs 15 lakh for joint accounts.
- Mahila Samman Saving Certificate, a one-time new saving scheme for women to be made available for two years up to March 2025.
Sector-wise highlights
1. Banking
Govt makes amendments to Banking Regulation Act to improve governance in banks.
2. Jobs
- The government will launch Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana 4.0 to enable much Indian youth to take up industry-relevant skill training.
- Similarly 30 Skill India International Centers will be set up across different States to upskill the youth for international opportunities.
3. Infrastructure & Investments
- Creating urban infrastructure in Tier 2 and Tier 3 cities via establishing UIDF.
- Increased capital investment outlay by 33.4% to Rs.10 lakh crore.
- Continuation of a 50-year interest-free loan to State governments to incentivize infrastructure investment.
- Highest ever capital outlay of Rs.2.4 lakh crore for Railways
4. Energy & Environment
- Rs 35,000 crores priority capital for the energy transition.
- Battery Energy Storage Systems with 4,000 MWh capacity will be supported with viability gap funding.
- Companies, individuals, and local bodies will be eligible for a Green Credit Programme under the Environment (Protection) Act of 1986 to encourage and collect resources for environmentally sustainable actions.
- For funds to be allocated for replacing old polluted vehicles.
- Moreover Setting up 10,000 bio inputs resource centres to facilitate farmers to adopt natural farming.
5. Health
- One hundred fifty-seven new nursing colleges are going to establish.
- Sickle cell anaemia elimination mission is going to launch covering seven crore people in the age group 0-40 in affected tribal areas.
- A new programme to promote research in pharmaceuticals will be launching.
6. Education
- National Digital libraries are to be set up for children and adolescents.
- States to set up physical libraries at panchayat and ward levels.
- Revamped teacher’s training via District Institutes of Education and Training.
7. Agriculture
- An Agriculture Accelerator Fund will set up to encourage agri-startups in rural areas.
- Also a sub-scheme of PM Matsya Sampada Yojana will launch with an investment of Rs 6,000 crore to support fishermen, fish vendors, and MSMEs.
- Decentralized storage capacity will set up for farmers to store their produce.
- 20 lakh crore agricultural credit targeted at Animal husbandry, Dairy and fisheries sector.
8. Finance
- Setting up National Financial Information Register to enable efficient lending, promote financial inclusion and enhance financial stability.
- Similarly setting up a Central data processing centre for faster handling of administrative work under the companies act.
9. Urban development
- An Urban Infrastructure Development Fund will establish to develop urban infrastructure by public agencies in tier-2 and tier-3 cities.
- States and cities will encourage to undertake urban planning reforms such as efficient land use and transit-oriented development.
10. Research And Development (R&D)
- Three centres of excellence for R&D in Artificial Intelligence (AI) will establish in select educational institutions.
- Surely 100 labs will set up in engineering institutions for developing 5G applications.
11. Sports
- Rs 3,397.32 crore is allocated to Sports, an increase of Rs 723.97 crore and the country’s highest-ever sports budget allocation.
- Moreover National sports federation (nsfoi) gets a hike of Rs.325 crore.
- Sports Authority of India (SAI) receives Rs.785.52 crore.
- Also 1,045 crore is allocated to ‘Khelo India’.
12. Space
- Department of Space has been allocated Rs.12,544 crore.
- Rs 408.69 crore is allocated to Physical Research Laboratory.
Budget Estimates of 2023-24
- Total Expenditure: Clearly the government estimate to spend Rs 45,03,097 crore in 2023-24, an increase of 7.5% over the revised estimate of 2022-23.
- Revenue Expenditure: Out of the total expenditure, revenue expenditure estimate to be Rs 35,02,136 crore, an increase of 1.2%.
- Capital Expenditure: Capital expenditure estimate to be Rs 10,00,961 crore, which is a 37.4% increase. The increase in capital expenditure is due to an increase in capital outlay on transport (including railways, roads and bridges, and inland water transport) by Rs 1,28,863 crore (36.1% increase).
- Total receipts: Government receipts (borrowings excluded) are estimated to be Rs 27,16,281 crore, an increase of 11.7% over the revised estimates for 2022-23.
- Estimated GDP growth: The nominal GDP will grow at 10.5% in 2023-24.
- Transfer to states: The central government will transfer Rs 18,62,874 crore to states and union territories. Thus an increase of 8.9% over the revised estimates for 2022-23.
Check our Year In Review 2022 blog, where we cover all the major events and highlights of the business and tech world in the year 2022.