SVB Collapse
What was Silicon Valley Bank ?
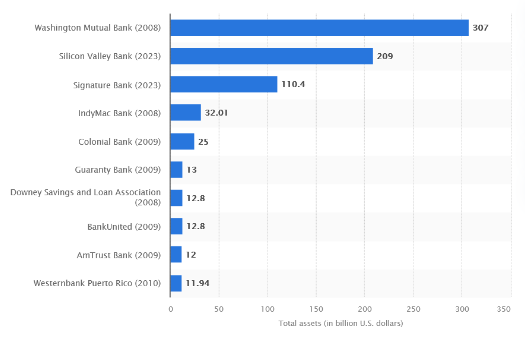
Silicon Valley Bank is a state-chartered commercial bank headquartered in Santa Clara, California, that failed on March 10, 2023, and its assets are now under the care of the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC). It was the 16th-largest bank in the U.S. and Silicon Valley’s largest bank based on deposits. The bank mainly comprises the primary business of SVB Financial Group, a publicly traded bank holding company with other subsidiaries.
History Of Silicon Valley Bank
Silicon Valley Bank was founded in 1983 in San Jose, California, by Bill Biggerstaff, Robert Medearisa, and Robert Smith.
The company went public in 1988 and eventually grew to be one of the largest commercial banks in the U.S. It saw major growth during and after the pandemic between 2019 and 2022, where it rose from the 34th largest bank to the 16th.
Why did Silicon Valley Bank collapse?
As Silicon Valley Bank was founded, the banking industry needed a better understanding of startups, especially those that didn’t generate revenue. Startups wait for income, so the bank structured its loans to manage risk based on business models.
The bank connected customers to its extensive venture capital, law, and accounting firm network. Its primary strategy was collecting deposits from businesses financed through venture capital. It was then expanded into banking and financing venture capitalists by adding services to allow the bank to keep clients when they mature from their startup phase. Initially, startup founders seeking bank loans pledged about half their shares as collateral. After a few years, the failure rate dropped to about seven per cent, reflecting low failure rates and founders’ willingness to pay back their loans. The bank covered the losses by selling the shares to interested investors. Eventually, it became typical for venture capital firms’ term sheets to the requirement of startups to create a bank account at SVB specifically.
The significant increase in interest rates is a recurring theme in the failure of SVB. The U.S. Federal Reserve has quickly raised its benchmark policy rates from the historically low levels of last year to combat inflation. This expected to reach a 40-year high in 2022 and cause the economy to slow down and investments to decline.
Investors that pour money into riskier investments when cheaper typically have a poor risk tolerance in an environment with high interest rates. Most of SVB’s clients, startups, saw a big decline in their investments as interest rates kept rising.
The Reason The Bank Forced To Sell Its Holdings At a Loss:
Major venture capitalists (VCs), who had sizable accounts with the bank and were SVB’s clients, provided the majority of the funding for early-stage firms. SVB’s deposits increased thrice to $189.20 billion in 2021 amidst the VC industry boom. However, since the IPO Boom ended in 2022, there weren’t many withdrawals. The bank’s loan operations could not keep up with the deposit surge. As a result, the bank bought over $80 billion in mortgage-backed securities (MBS) with these deposits for its hold-to-maturity (HTM) portfolio – with an average yield of 1.56%.
These MBS lost value due to the US central bank’s continued raising interest rates. This resulted from investors’ ability to purchase long-term “risk-free” bonds from the Fed for a 4-5% yield. Nine times in 2022, the US Federal Reserve raised interest rates steadily to rein in inflation. Bond yields often increase as interest rates rise. Due to their safety, yields become more appealing than equities after crossing a certain threshold. Bonds became more appealing to investors due to growing interest rates and yields, which decreased the value of the bonds owned by banks. Bond prices and yields have the opposite relationship.
Why did they rush to the bank?
It is hard to nail down the precise cause of a run; crowd psychology is at play. Yet after the bank announced a capital raise and the sale of a large fraction of securities at a loss, concerns might have surfaced. The bank catered to startups in the technology and venture capital. Because they were corporate deposits, several exceeded the $250,000 insurance cap the Federal Deposit Insurance Corp set. SVB’s uninsured deposits exceeded more than $150 billion at the previous year’s end.
Several SVB clients started withdrawing money from the bank to fulfil their liquidity needs. Interest rates forced initial public offerings, another method of raising capital for startups, to come to a screeching halt in the US. To continue allowing withdrawals, the lender was compelled to look into its alternatives for raising money. In the hours before the bank’s collapse, the run worsened as several startups attempted to withdraw money. Many failed while others were successful, which exacerbated the fear and compelled the FDIC to take charge.
SVB Might Have Been Able To Hold Onto Paper Losses Until Rates Fell
The bank might have theoretically gotten by letting securities mature and getting its money back. It’s possible that until things changed, deposits were being released rather steadily. But, after a spike in deposit withdrawals, it didn’t have that time.
The bank then faced a tidal wave of $42 billion in deposit withdrawal requests last week. It failed to raise funds needed to cover the outflows, prompting regulators to respond with force.
Unsuccessful fundraising effort
SVB liquidated a $22 billion bond portfolio made up primarily of US Treasuries, whose values had fallen due to the Fed’s tightening of monetary policy, in an effort to pay for the redemption. The lender was compelled to record a $1.8 billion loss. SVB attempted to close the gap by financing $2.25 billion by selling preferred convertible stock and equity but was unsuccessful. The lender rushed to secure alternative finance on Friday by selling the business.
Where did the uninsured deposits end up?
The FDIC announced on Friday that SVB-insured depositors would have access to their money by Monday am at the latest. The original statement stated that uninsured depositors would first receive a dividend and then receivership certificates for any outstanding balances that might be paid out over time, implying that payback wasn’t guaranteed. But then, on Sunday, the FDIC said it would use a “systemic risk exemption” to cover the uninsured deposits of SVB and Signature, together with the Treasury Department and Secretary Janet Yellen, and President Biden. On Monday morning, customers could also access their deposits.
Immediate Impact: VC Market
The immediate impact of inaccessible bank accounts on the VC market Startups that kept operating funds with SVB would have experienced an existential crisis. Due to a significant lack of available cash induced by the delayed fund raising climate, the VC sector was already in a complicated situation. The good news was that business were able to access the total amount of their deposits on Monday, for the beginning of a successful operation. With a backup finance plan, many firms could get capital quickly. The $152.0 billion in uninsured deposits SVB includes startup companies’ working capital.
There was an immediate operational issue for businesses that need to pay wages or pay for the usage of services, whether or not all that capital was eventually recovered. Investors would have major impact by the loss of portfolio firms. Not just by corporate closures, had access to this money been lost. Due to limited partners’ lowered confidence in the venture market due to these losses, there would have been fewer investment vehicles available and a more pronounced decline in short term venture funding.
Impact on Depositors and Investors
Bank deposits of up to $250,000 per depositor per bank for each account section undergo insured by FDIC. Silicon Valley Bank accounts with $250,000 deposits would get their money back. Unfortunately, most of the funds in Silicon Valley Bank were uninsured as they had more than $250,000 of deposits.
However, investors won’t be so lucky, as those who own stock in SVB Financial Group may not get their money back.
Implications for the venture lending market
The abrupt fall of SVB significantly impacts VC-backed start ups that currently hold a loan contract with the bank. Especially when it is unclear when the bank will get sold and whether existing loan terms and conditions will be honoured when an acquirer steps in. SVB has provided debt solutions to start ups across the venture ecosystem, ranging from pre-revenue, early-stage startups to late-stage ones, with up to $75 million in recurring revenues. In 2022, SVB issued $6.7 billion of venture debt, making up 9% of its loan portfolio. This type of debt is “investor-dependent” (ID), meaning that loan origination is contingent upon the existing investors’ commitment to a company’s future success.
The bank’s collapse has had a particularly detrimental effect on early-stage startups that have yet to develop vital financial metrics and primarily rely on their investor syndicate to secure debt. For years, startups in nascent stages of development had access to term loans from SVB with low-interest rates and ample structural flexibility. With its collapse, early-stage startups without a steady revenue stream will likely encounter severe headwinds seeking alternative debt financing. Late-stage companies, on the other hand, face a different set of issues. Not only do these companies require larger loan packages, which makes borrowing from debt funds even more costly, but the private credit market, a significant player in debt financing for companies operating at a more developed stage, also faces market uncertainty. This is thus adding another layer of challenges. Percentage-wise, the bank has been shrinking the weight of its venture debt portfolio.
Timeline Of The Collapse
The SVB crash happened rapidly throughout just a couple of days. Following is a timeline of events:
March 8: SVB announced its $1.8 billion loss on its bond portfolio and planned to sell both common and preferred stock to raise $2.25 billion.
March 9: The stock of SVB Financial Group, which is the holding company of SVB, crashed at the market opening. Other major banks’ stock prices also took a hit.
March 10: SVB Financial Group stock trading gets halted. Federal regulators announced a takeover of the bank.
March 17: The parent company of Silicon Valley Bank, SVB Financial Group filed for bankruptcy.
March 26: First Citizens Bank acquired all of Silicon Valley Bridge Bank except for $90 billion of securities and other assets that remained in FDIC receivership.
Source :S&P CApital IQ
Key takeaways
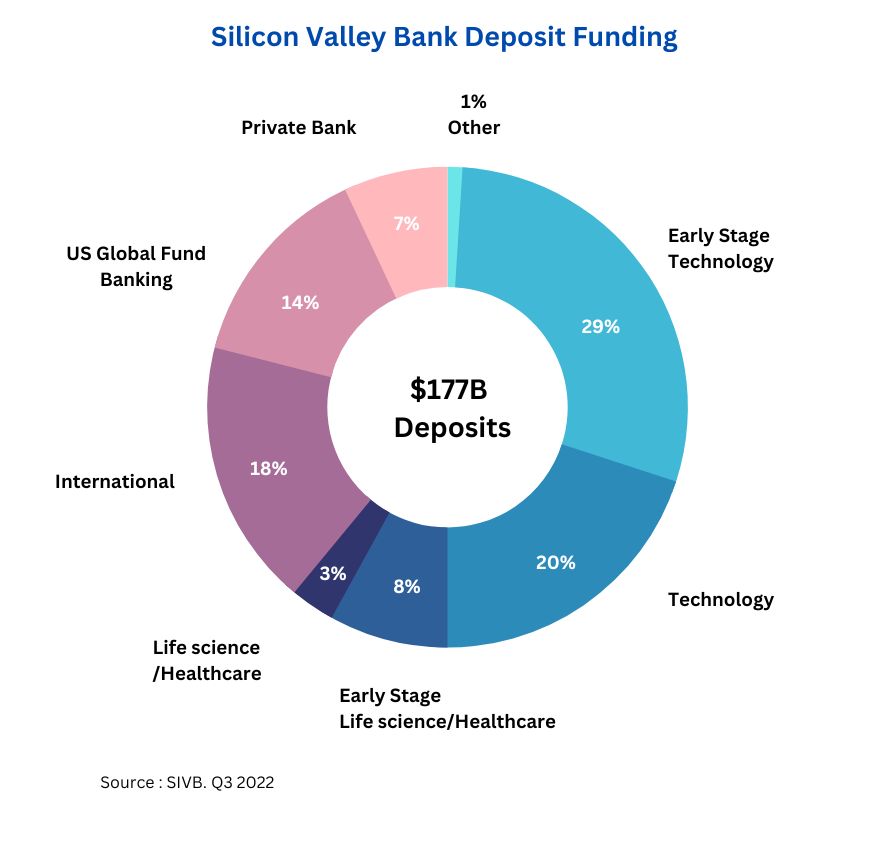
• Over nearly 40 years, SVB has become many successful venture startups’ leading lenders and banking partners. This brand recognition and trust resulted in SVB amassing more than $175 billion in total deposits. Since liquidity options for many startups dried up, these enterprises began to rely heavily on fund withdrawals from their bank accounts to extend the runway. To fund these withdrawals, SVB forced to sell many Treasuries and other securities. This devalued due to recent interest rate hikes. Fearing for the safety of their capital, depositors began to withdraw their funds in bulk. SVB could not fulfil withdrawal requests, and the FDIC seized the bank on March 10. Fortunately, the Fed assured all depositors that 100% of their capital would be safe and accessible by Monday.
• SVB’s failure further tightens the squeeze on an already sluggish venture market. Quarterly capital invested fell over 60%. And the deal count was down almost 25%, despite high relative numbers on a historical basis. Re-allocating resources and banking will only lead to a further slowdown in the financing market in Q1 2023. Bank loans were mostly made to GPs in both VC and PE. Thus allowing these funds to access capital more quickly for deals.
• The lightning strike of SVB’s collapse led to concerns over a possible contagion effect. Mainly on other regional banks collectively suffering from the same unintended consequences of the Fed’s interest rate hikes. Now that the lender of choice for many investors for decades suddenly gone. So it expects to see startups and investors looking to raise funds from non-bank lenders. While it remains unclear what will happen to companies with loan contracts with SVB. As an acquisition is yet to announce, VC-backed startups rush to raise debt from non-bank entities may push prices higher.
• Besides SVB’s venture debt portfolio wasn’t the primary cause of the bank’s abrupt fall, the critical role the bank has been playing in venture lending. It sounded alarms to active players in the venture market. For example, Hercules Capital is one of the largest business development companies that focus on venture lending. It released a business update in response to SVB’s collapse on Monday morning. Venture debt lenders will likely receive intensified inquiries and closer scrutiny in the short term.
What is creeping up next?
The sale of SVB proceedings will be under careful observation. The focus will also shift to longer-term concerns about the soundness of banks that investors are already raising. If interest rates continue where they are, the Fed’s borrowing facility may address immediate liquidity needs. Still, it won’t be able to restore the value of banks’ securities portfolios. In many ways, banks had slipped Washington’s attention in the years following the financial crisis.
FAQs
1.)What led to the failure of Silicon Valley Bank?
The bank’s balance sheets were overexposed, causing it to sell bonds at a loss to pay the withdrawal. And its biggest customers withdrew deposits rather than borrow at higher interest rates, which caused the bank to go bankrupt.
2.)Why did Signature Bank and Silicon Valley Bank fail?
Clients of SVB were withdrawing deposits faster than the bank could cover them with cash reserves, so it opted to sell $21 billion of its securities portfolio at a $1.8 billion loss to meet its obligations. The lender tried to raise more than $2 billion in new capital due to the drain on equity capital.
3.)What occurs to SVB staff members? Can SVB bounce back?
Key executives were fired, including Greg Becker, the CEO. Regulators are currently unwinding the bank and asking a lot of other staff to perform the same duties as they did before. Regulators may attempt to reclaim funds used to cover deposits by selling the bank. The SVB Financial Group’s larger business also include other areas that may auctioned off, like an investment bank.
4.)Could the bankruptcy of SVB trigger a recession?
The unsecured deposit guarantee may limit immediate effects, such as businesses holding money at SVB. Yet, lending that would tie up their resources could restricted if other banks are concerned about their capital or deposits. Still, the events altering the Federal Reserve’s rate of interest rate hikes is a key question.